Configuration of virtual machines
Used versions
- Ubuntu 10.04 x86 as guest OS
- Windows XP Professional 5.1.2600, Service Pack 3 as host OS
- VMware® player 3.0.0 build-203739
Configuration of network bridge
Benefits:
- No configuration necessary
- Guest is member in the net
Drawback:
- Guest is in the net like a “normal” host
Configuration of the target
The IP address of the virtual machine must be registered as the server IP in the target.
Configuration of NAT (Network Address Translation)
Access to NFS or TFTP of the virtual machine does not work.
Benefits:
- Guest is not reachable from the network
- Guest can access network via NAT
Drawback:
- Configuration very complex
Configuration of the target
The IP address of the host must be registered as the server IP in the target.
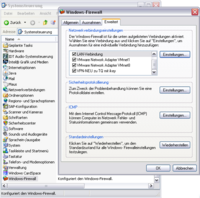
Configuration of Windows XP for port forwarding
The settings of the port forwarding can be done in the Windows Firewall. Go to the “Advanced” tab and select the LAN connection which connects the host and the target. Click on “Settings”.
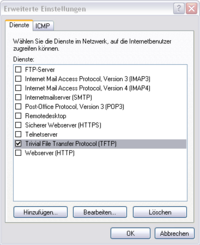
In the following window click on “add” and enter the necessary details.
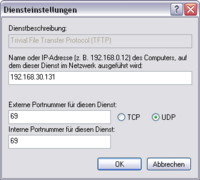 For TFTP this is the following data:
For TFTP this is the following data:
- Service description: Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
- Name or IP address: enter the IP address of the virtual machine
- External and internal port number: 69 UDP
Copying of virtual machines
When copying virtual machines, it may be that a new Ethernet device with a new MAC address is created. If the Ethernet device gets a new name (eth2 …), you have to add auto to the name of the interface in the file etc/network/interfaces (e.g., auto eth2). Then the service networking must be restarted (sudo service networking restart).
Alternatively, you can edit the file /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules and assign the MAC to the eth0 device.