Embedded module TQMa6ULxL - YOCTO Linux BSP documentation
Starterkit Interfaces and Functions
Audio
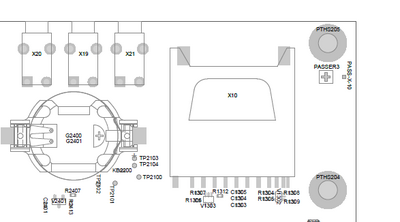
Audio Connector Overview
| Connector | Function |
|---|---|
| X19 | Microphone |
| X20 | Line In |
| X21 | Line Out |
Audio Connector Location
Play Audio on
A simple test sound can be played with the commandline tool speaker-test.
Headphones or active speakers have to be connected to X21 on .
speaker-test --channels 2 --test wav -D sysdefault:CARD=tqtlv320aic32x
You can also play your own audio files using aplay
aplay <file>
e.g.
aplay test.wav
Record Audio via Line-In on
arecord -f cd test.wav
amixer or alsamixer
“|mb_name=“MBa6ulx”|dipdescription=“DIP switch S3 is used to configure the CAN interfaces CAN0 and CAN1.”|dip1=“S3-1”|dip2=“S3-2”|can_image=” “}}
“}}
Ethernet
The STKa6ulxL Starterkit provides two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
U-Boot
In U-Boot eth0 is configured as default interface. The IP configuration can be done statically or by a DHCP server in the network.
IP configuration via DHCP
For a configuration via a DHCP server, use the dhcp command in U-Boot.
Static IP configuration For a static IP configuration the following, U-Boot environment variables must be set:
setenv ipaddr <ipaddr> (e.g.: setenv ipaddr 192.168.100.111) setenv netmask <netmask> (e.g.: setenv netmask 255.255.255.0)
Linux
Both Ethernet interfaces are activated and configured by systemd-network. The configuration files for interfaces are located in /lib/systemd/network/ these configuration files can be altered to customize the default interface configuration. A documentation of the configuration files can be found here.
For a temporary static configuration the ip command can be used, below some useful ip commands are listed:
Activate a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip link set eth0 up
Disable a specific interace
e.g. eth0
ip link set eth0 down
Show ip address for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip addr show eth0
Show statistic for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip -s link show eth0
Set ip address for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip addr add 192.168.1.100/24 dev eth0
Show statistic of all interfaces
ip -s link
Set default gateway for a specific interfaces
e.g. set gateway ip 192.168.1.1 for eth0
ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 dev eth0
If a DHCP server is available in the network environment the ip configuration can be received from it. To do so execute the udhcpc command, by default eth0 is used.
To configure another interface via dhcp the parameter -i followed by the interface name e.g. eth1 must be given.
e.g. eth1
udhcpc -i eth1
I2C
An overview of the onboard i2c devices is available here
U-Boot
Select i2c bus device
i2c dev 3
Show all devices connected to the i2c bus currently selected:
i2c probe
Linux
Detect all devices connected to a i2c bus:
i2cdetect 3
LVDS
TQ offers an optional LVDS Display kit for the STKa6ulxL. Each Display can be used on its own by using the corresponding device tree. To allow reusage, the support for each display is separated in a dtsi fragment.
To bring up the display the U-Boot environment has to be adapted accordingly.
- Interrupt boot process in U-boot
- Set U-Boot environment variable fdtfile with the command
setenv fdtfile <device tree>(e.g.setenv fdt_file imx6ul-mba6ulx-lga-lvds.dtb) - Save the envrionment by executing the
saveenvcommand
RTC
To set the hardware clock to the actual time and date use the following commands:
date -s [YYYY.]MM.DD-hh:mm[:ss] hwclock -w
SPI
The MBa6ulx has one SPI interfaces. They can be found on the extension headers and can be tested with a loopback test.
SPI Overview
| Interface | linux filesystem |
|---|---|
| SPI2 | /dev/spidev1.0 |
Loopback Test SPI Interface
For the loopback test you need a bridge between SPI_MOSI and SPI_MISO:
- SPI2: bridge between X5_35 (SPI2_MOSI) and X5_36 (SPI2_MISO)
echo -n -e "\x01\x0F" | spi-pipe -d <spi interface> -s 10000000 | hexdump (e.g. echo -n -e "\x01\x0F" | spi-pipe -d /dev/spidev1.0 -s 10000000 | hexdump)
Temperature Sensors
@temp_description@ @temp_sensors@
USB
With lsusb you can see all connected usb devices. To mount a partition of an usb stick you can excute mount /dev/<partition> <mount dir> (e.g. mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt). This will mount the first partition of sdb to /mnt. To unmount the device execute umount <mount dir> (e.g. umount /mnt).
User LED
The MBa6ulx has two user controllable LEDs, the behavior of these LEDs can be selected by several triggers.
User LED Overview
| Reference | LED name | color | linux filesystem |
|---|
User LED Location
“{{ :en:arm:tqma6ulx:linux:yocto:mba6ulx_user_led.png?nolink&400 |
The user LED's are located in .
To change the behaviour a specific LED, the value in the file trigger must be overwritten.
The following values are valid:
For example set the trigger of to heartbeat
echo heartbeat >
“|userled_location=”/sys/devices/soc0/gpio-leds/leds”|led_example=“led1”|userled_example=“/sys/class/leds/led1/trigger”}}