Embedded module TQMLS10xxA - YOCTO Linux BSP documentation
Starterkit Interfaces and Functions
Buttons
There are two GPIO buttons on the MBLS10xxA. They are bound to the gpio-keys driver, and can be tested with the evtest tool.
GPIO Button Overview
| Reference | Button |
|---|
GPIO Button Location
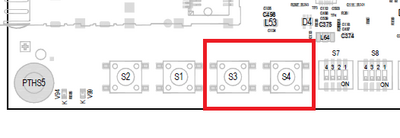
The buttons are available in the sysfs via the device and can be tested with the evtest tool.
“|button_device=”/dev/input/event0“|button_test=“evtest /dev/input/event0”}}
Ethernet TQMLS1043A
The STKLS1043A provides one 10 Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces and eight 10/100/1000 Ethernet Interfaces.
U-Boot
In U-Boot FM1@DTSEC3 is configured as default interface. The IP configuration can be done statically or by a DHCP server in the network. IP configuration via DHCP
For a configuration via a DHCP server, use the dhcp command in U-Boot.
Static IP configuration For a static IP configuration the following, U-Boot environment variables must be set:
setenv ipaddr <ipaddr> (e.g.: setenv ipaddr 192.168.100.111) setenv netmask <netmask> (e.g.: setenv netmask 255.255.255.0)
Linux
All Ethernet interfaces are deactivated by default. To activate the interfaces use the following command.
For a temporary static configuration the ip command can be used, below some useful ip commands are listed:
Activate a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac2
ip link set fm1-mac2 up
Disable a specific interace
e.g. fm1-mac2
ip link set fm1-mac2 down
Show ip address for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac2
ip addr show fm1-mac2
Show statistic for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac2
ip -s link show fm1-mac2
Set ip address for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac2
ip addr add 192.168.1.100/24 dev fm1-mac2
Show statistic of all interfaces
ip -s link
Set default gateway for a specific interfaces
e.g. set gateway ip 192.168.1.1 for fm1-mac2
ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 dev fm1-mac2
If a DHCP server is available in the network environment the ip configuration can be received from it. To do so execute the udhcpc command, by default eth0 is used.
To configure another interface via dhcp the parameter -i followed by the interface name e.g. fm1-mac2 must be given.
e.g. fm1-mac2
udhcpc -i fm1-mac2
Ethernet TQMLS1046A
The STKLS1046A provides two 10 Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces and eight 10/100/1000 Ethernet Interfaces.
Ethernet Interface Assignment
For the ethernet interface assignment see here.
How to use 10Gbit ethernet on STKLS1046
In order to use the two 10 Gbit ethernet interfaces on the STKLS1046, the U-Boot bootloader has to be rebuilt with a new RCW configuration.
By default RCW 3333 (SerDes1) and 5559 (SerDes2) are configured in the TQMLS1046 U-Boot. This RCW configuration does not support 10Gbit ethernet.
RCW Configuration 1133_5559
As an example the RCW configuration 1133(SerDes1) and 5559(SerDes2) has been chosen for this how to.
See the tables below for further information about the RCW configuration.
| SerDes1 - RCW 1133 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lane D | Lane C | Lane B | Lane A | PCIe GEN1/2 PLL Mapping | PCIe GEN3 PLL Mapping |
| XFI.9 | XFI.10 | SGMII.5 | SGMII.6 | 2211 | N/A |
| SerDes2 - RCW 5559 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lane D | Lane C | Lane B | Lane A | PCIe GEN1/2 PLL Mapping | PCIe GEN3 PLL Mapping |
| Unused | PCIe.2 x1 | PCIe.3 x1 | SATA | 2221 | N/A |
Rebuild U-Boot with RCW configuration 1133_5559
- After building the Yocto Image, following line has to be added to configuration file local.conf
RCWSD = "default/rcw_1800_1133_5559_sd"
RCWQSPI = "default/rcw_1800_3333_5559_qspi"
- Create a new Image with the following command:
bitbake core-image-minimal
STKLS1046 DIP Switch Configuration
According to the RCW 1133_5559 the DIP switches on STKLS1046 DIP must be set as follows:
SD card RCW 1133_5559
| S7 | S8 | S6 | S5 | S10 | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIP | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| OFF | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | |||||||||||||
| ON | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | |||||||||||||||
Ethernet interface assigment RCW 1133_5559
U-Boot
In U-Boot FM1@DTSEC3 is configured as default interface. The IP configuration can be done statically or by a DHCP server in the network. IP configuration via DHCP
For a configuration via a DHCP server, use the dhcp command in U-Boot.
Static IP configuration For a static IP configuration the following, U-Boot environment variables must be set:
setenv ipaddr <ipaddr> (e.g.: setenv ipaddr 192.168.100.111) setenv netmask <netmask> (e.g.: setenv netmask 255.255.255.0)
Linux
All Ethernet interfaces are deactivated by default. To activate the interfaces use the following command.
For a temporary static configuration the ip command can be used, below some useful ip commands are listed:
Activate a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac3
ip link set fm1-mac3 up
Disable a specific interace
e.g. fm1-mac3
ip link set fm1-mac3 down
Show ip address for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac3
ip addr show fm1-mac3
Show statistic for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac3
ip -s link show fm1-mac3
Set ip address for a specific interface
e.g. fm1-mac3
ip addr add 192.168.1.100/24 dev fm1-mac3
Show statistic of all interfaces
ip -s link
Set default gateway for a specific interfaces
e.g. set gateway ip 192.168.1.1 for fm1-mac3
ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 dev fm1-mac3
If a DHCP server is available in the network environment the ip configuration can be received from it. To do so execute the udhcpc command, by default eth0 is used.
To configure another interface via dhcp the parameter -i followed by the interface name e.g. fm1-mac3 must be given.
e.g. fm1-mac3
udhcpc -i fm1-mac3
Ethernet TQMLS1088A
The STKLS1088A provides two 10 Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces and eight 10/100/1000 Ethernet Interfaces.
Ethernet Interface Assignment
For the ethernet interface assignment see here.
Ethernet Interface Configuration
The Ethernet interfaces are managed via DPAA2 and not configured by default. The interfaces have to be configured in Linux:
ls-addni dpmac.X
Example configuration of DPMAC2:
ls-addni dpmac.2
Afterwards you can save the configuration to a dts file with:
restool dprc generate-dpl dprc.1 > <my_dpl>.dts
To generate a dtb file you have to use
dtc -I dts -O dtb <my_dpl>.dts -o <my_dpl>.dtb
Copy the generated dtb file to the boot partition (/dev/mmcblk0p1) and execute in U-Boot the following commands with your dtb file name
setenv dpl_file <my_dpl>.dtb
load mmc ${mmcdev}:1 $loadaddr ${dpl_file}
mmc write ${loadaddr} 0x6800 0x800
U-Boot
In U-Boot DPMAC4@rgmii-id is configured as default interface. The IP configuration can be done statically or by a DHCP server in the network. IP configuration via DHCP
For a configuration via a DHCP server, use the dhcp command in U-Boot.
Static IP configuration For a static IP configuration the following, U-Boot environment variables must be set:
setenv ipaddr <ipaddr> (e.g.: setenv ipaddr 192.168.100.111) setenv netmask <netmask> (e.g.: setenv netmask 255.255.255.0)
Linux
With the right dtb configuration file all ethernet interfaces are activated.
For a temporary static configuration the ip command can be used, below some useful ip commands are listed:
Activate a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip link set eth0 up
Disable a specific interace
e.g. eth0
ip link set eth0 down
Show ip address for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip addr show eth0
Show statistic for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip -s link show eth0
Set ip address for a specific interface
e.g. eth0
ip addr add 192.168.1.100/24 dev eth0
Show statistic of all interfaces
ip -s link
Set default gateway for a specific interfaces
e.g. set gateway ip 192.168.1.1 for eth0
ip route add default via 192.168.1.1 dev eth0
If a DHCP server is available in the network environment the ip configuration can be received from it. To do so execute the udhcpc command, by default eth0 is used.
To configure another interface via dhcp the parameter -i followed by the interface name e.g. eth1 must be given.
e.g. eth1
udhcpc -i eth1
I2C
An overview of the onboard i2c devices is available here
U-Boot
Select i2c bus device
i2c dev [0,2,3]
Show all devices connected to the i2c bus currently selected:
i2c probe
Linux
Detect all devices connected to a i2c bus:
i2cdetect [0,1,2,3]
RTC
To set the hardware clock to the actual time and date use the following commands:
date -s [YYYY.]MM.DD-hh:mm[:ss] hwclock -w
Temperature Sensors
@temp_description@ @temp_sensors@
USB
With lsusb you can see all connected usb devices. To mount a partition of an usb stick you can excute mount /dev/<partition> <mount dir> (e.g. mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt). This will mount the first partition of sdb to /mnt. To unmount the device execute umount <mount dir> (e.g. umount /mnt).
User LED
The MBLS10xxA has one user controllable LEDs, the behavior of these LED can be selected by several triggers.
User LED Overview
| Reference | LED name | color | linux filesystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| V78 | led:user | green | /sys/class/leds/led\:user/trigger |
User LED Location
“{{ :en:layerscape:tqmls10xxa:linux:yocto:mbls10xxa_user_led.png?nolink&400 |
The user LED's are located in .
To change the behaviour a specific LED, the value in the file trigger must be overwritten.
The following values are valid:
For example set the trigger of to heartbeat
echo heartbeat >
“|userled_location=”/sys/devices/platform/leds/leds/“|userled_example=”/sys/class/leds/led\:user/trigger”}}
Updating existing firmware over ethernet
To update bootloader / kernel / devicetree in a running system you have to copy the images to a tftp directory and upload them to the eMMC or SD Card.
Please see How to setup TFTP Server
1. Boot Starterkit and interrupt boot process in U-Boot
Hit any key to stop autoboot: =>
3. Connect device via ethernet to the TFTP server which supplies the image
4. Provide the correct network configuration in U-Boot:
The manual network configuration must be done if no DHCP server is available, otherwise the configuration can be done via DHCP.
Manual network configuration
- ⇒ setenv autoload no
- ⇒ setenv serverip <serverip> (e.g.: setenv serverip 192.168.100.110)
- ⇒ setenv ipaddr <ipaddr> (e.g.: setenv ipaddr 192.168.100.111)
- ⇒ setenv netmask <netmask> (e.g.: setenv netmask 255.255.255.0)
Network configuration via DHCP
- ⇒ setenv autoload no
- ⇒ dhcp
5. Set U-Boot environment variables according to the image file name stored on the tftp server:
- For U-Boot update on eMMC/SD Card : ⇒ setenv uboot_mmc <filename> (e.g.: setenv uboot_mmc u-boot-with-spl-pbl.bin)
- For U-Boot update on QSPI NOR : ⇒ setenv uboot_qspi <filename> (e.g.: setenv uboot_qspi u-boot-pbl.bin.bswap )
- For Device Tree update on eMMC/SD Card and QSPI NOR : ⇒ setenv fdt_file <filename> (e.g.: setenv fdt_file fsl-tqmls1043a-mbls10xxa.dtb)
- For Kernel update on eMMC/SD Card and QSPI NOR : ⇒ setenv kernel <filename> (e.g.: setenv kernel linuximage)
6. Perform Update:
* U-Boot update on eMMC /SD Card : => run update_uboot_mmc * U-Boot update on QSPI NOR : => run update_uboot_qspi
- Device Tree update on eMMC /SD Card : ⇒ run update_fdt_mmc
- Device Tree update on QSPI NOR : ⇒ run update_fdt_qspi
- Kernel update on eMMC /SD Card : ⇒ run update_kernel_mmc
- Kernel update on QSPI NOR : ⇒ run update_kernel_qspi