Starterkit Quicksteps
The Starterkit STKaRZG2x consisting of the TQMaRZG2x module and MBaRZG2x mainboard is intended as evaluation platform for the TQMaRZG2x. To bring up the board a comprehensive set of accessories is supplied with the kit. The STKaRZG2x is delivered preconfigured to boot the latest released Linux BSP revision at the time of delivery, so only the Host Computer has to be set up properly to bring the STKaRZG2x up. This page guides through the first steps with the STKaRZG2x Starterkit.
Setup Host Computer
Serial Driver
The TQMaRZG2x debug UART is connected via a Silicon Labs USB-to-Serial converter to X9 (micro-USB) on the MBaRZG2x. A micro-USB/USB-A cable is part of the STKaRZG2x accessory set. Depending on the host operating system, a driver may need to be installed.
Linux
The driver is maintained in the Linux Mainline Kernel, please check that the following options are activated in the Linux Kernel configuration.
- CONFIG_USB_SERIAL
- CONFIG_USB_SERIAL_CP210X
Windows
The driver can be downloaded from the Vendor website:
https://www.silabs.com/developers/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers
Terminal Emulator
Linux
Minicom
Minicom is a command line based serial terminal for serial communication with hardware like our starterkits.
Install Minicom using APT(Debian/Ubuntu)
$ sudo apt install minicom
In order for the terminal to work properly with full rights you need to add your user to the dialout group:
$ sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
Connect Starterkit to Host
To determine the serial device name under linux you can use dmesg. Just run the command below and then plug in the starter kit to see the new detected interface names:
$ dmesg -w
Once the interface name is clear you can abort dmesg with ctrl + c.
Now you can start minicom via the command line interface:
$ minicom -D /dev/ttySx
Configure minicom
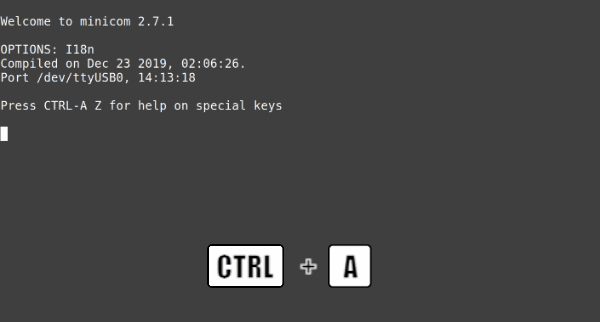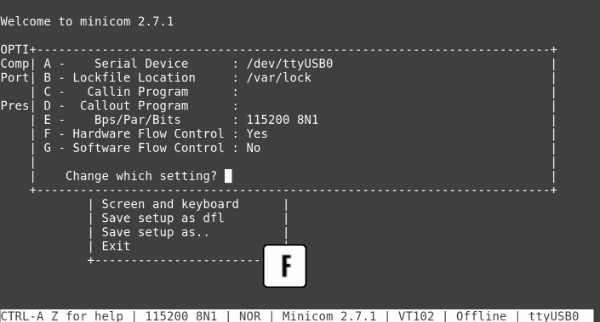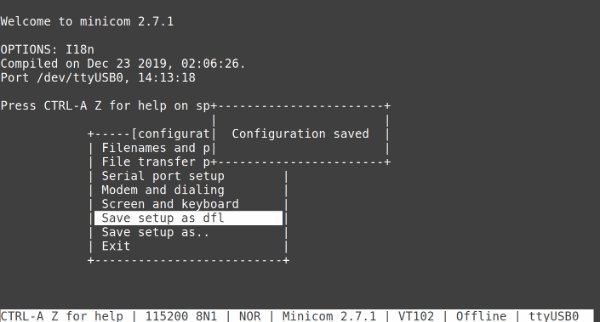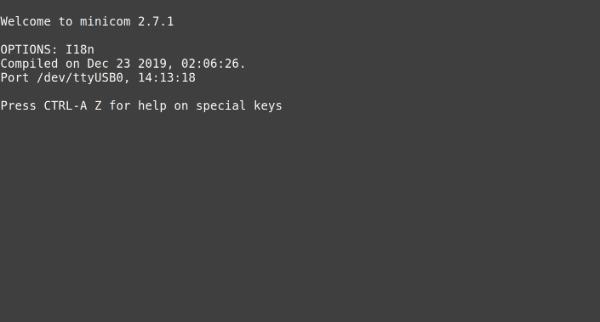
The serial configuration should be correct by default. However, hardware flow control must be disabled for some starter kits, otherwise the communication works only in one direction.
- Press CTRL + A, then press O to open the configuration menu
- Go to Serial port setup
- Press F to change Hardware Flow Control to No
- Hit Return key
- Select Save setup as dfl to save this configuration as default
- Press ESC to exit the menu
Windows
TeraTerm
TeraTerm is an open source terminal emulator for windows. it can be downloaded here.
Configure TeraTerm
- Download and install TeraTerm
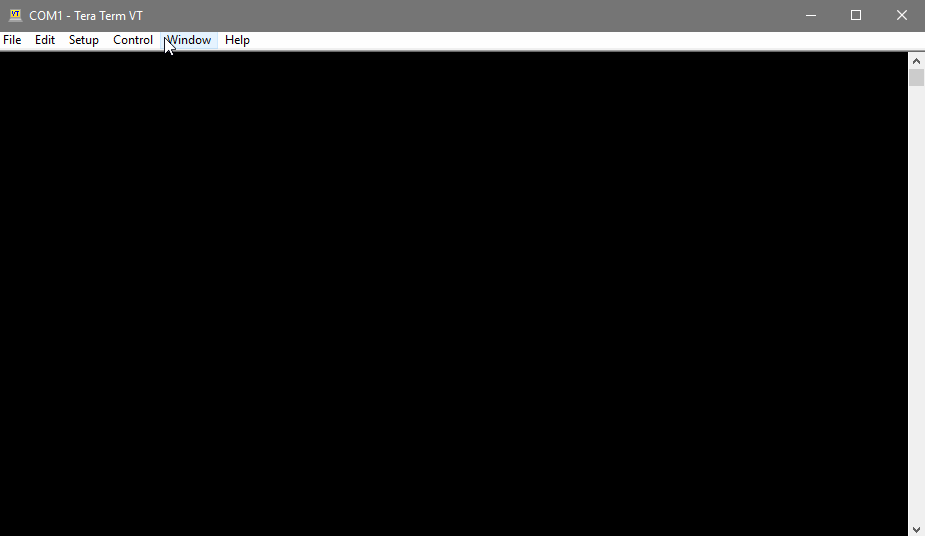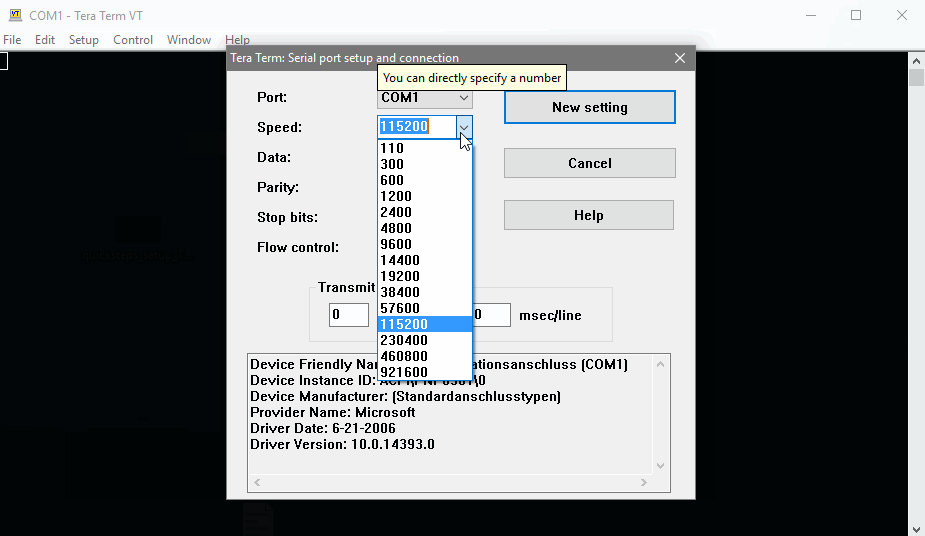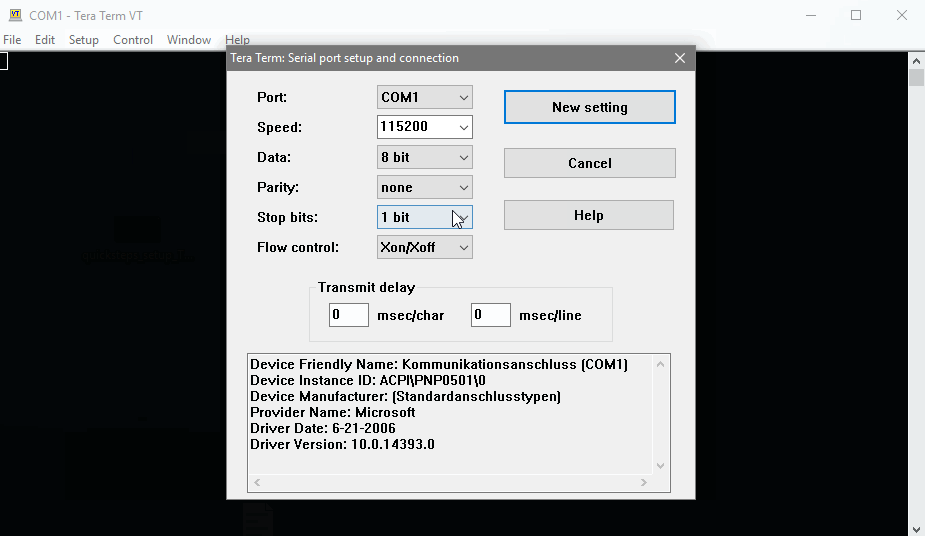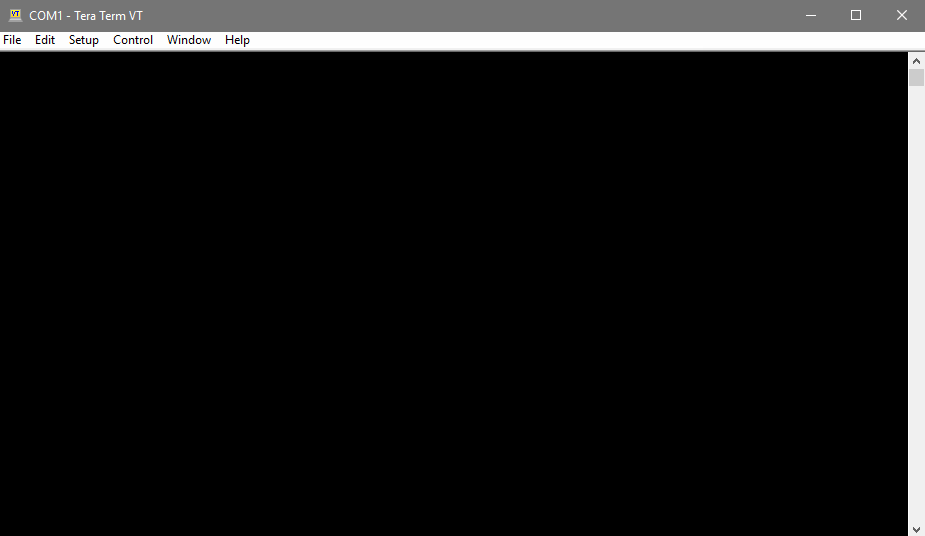
- Start TeraTerm and open the Serial Port Settings
- Select your serial port and configure it with the values defined in the chapter Serial Configuration
- After passing the values click on the button New Setting
Host PC Serial Port Configuration
The serial port which connects the STKaRZG2x to the Host PC must be configured as follows:
| Baud rate: | 115200 |
|---|---|
| Data bits: | 8 |
| Parity: | none |
| Stop bits: | 1 |
| Handshake: | XON/XOFF |
Connecting the Starterkit to the Development Host
Please follow the quick start guide delivered with the kit, or open it from the following link: Quick start guide
Linux
BSP Login Credentials
As soon as logging in on the Linux shell for the first time, the question about the login credential comes up.
By default the user root is used to log into the Linux shell, no password is set for user root.
tqmaxx-mbaxx login: root
Testing Interfaces on STKaRZG2x
To get familiar with the interfaces of the STKaRZG2x we recommend to work through the interface tutorials first.
Building the BSP
The Board Support Packages provided by TQ may not contain all software packages to evaluate the STKaRZG2x, therefore TQ provides some guides how to build the BSP and customize it for your needs:
In addition to the BSP documentation, the Yocto SDK build and Eclipse IDE setup for the STKaRZG2x is also documented.
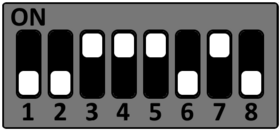
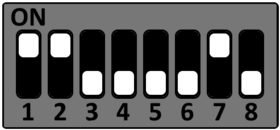
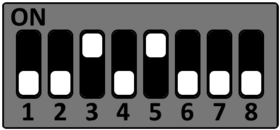
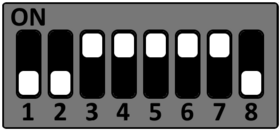
Setup Starterkit for different boot sources
The STKaRZG2x can be setup to boot from different sources. Please see the DIP switch settings below to change the boot source.